不管是做前端还是后端,都可能会遇到路由匹配的需求。如果是静态路由,可以直接用哈希表进行存储,查找时直接从哈希表查即可,速度非常快,复杂度 O(1)。
但在实际场景中,更多的是动态路由的匹配,动态路由直接用哈希表就有点力不从心了。动态路由可以用前缀树这个结构。
前缀树
前缀树(Trie 树)是一种树形结构,经常被用作单词前缀补全以及动态路由的匹配实现。
前缀树的特点:
- 根节点不包含字符,除根节点外的每一个子节点都包含一个字符。
- 从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串
- 每个节点包含的所有子节点包含的字符不同
- 从第一字符开始有连续重复的字符只占用一个节点
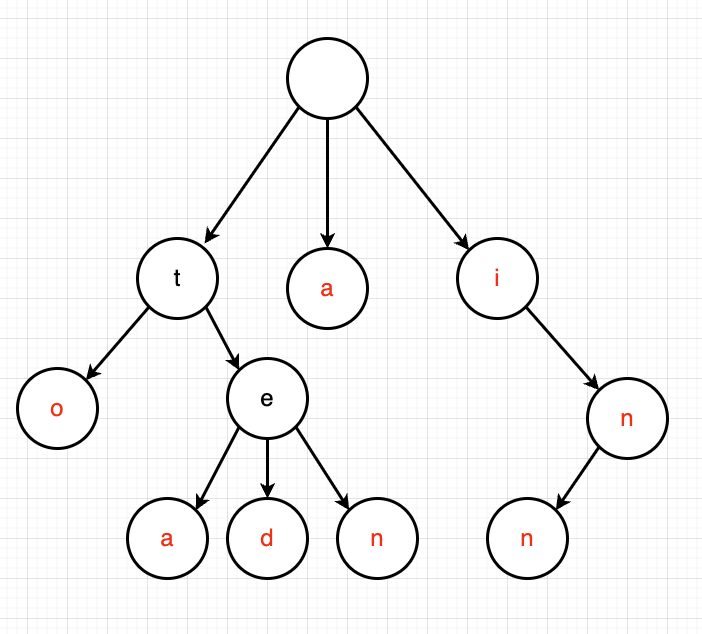
上图是一棵前缀树,表示了关键字集合 {“a”, “to”, “tea”, “ten”, “i”, “in”, “inn”}。
前缀树的基本实现
1 | // Trie节点 |
动态路由实现
基于前缀树这个结构,我们可以应用于路由的匹配。
比如下面这张图可以匹配如下的路由规则:
- GET /users
- GET /users/:id
- GET /about
- GET /blogs
- GET /blogs/:id
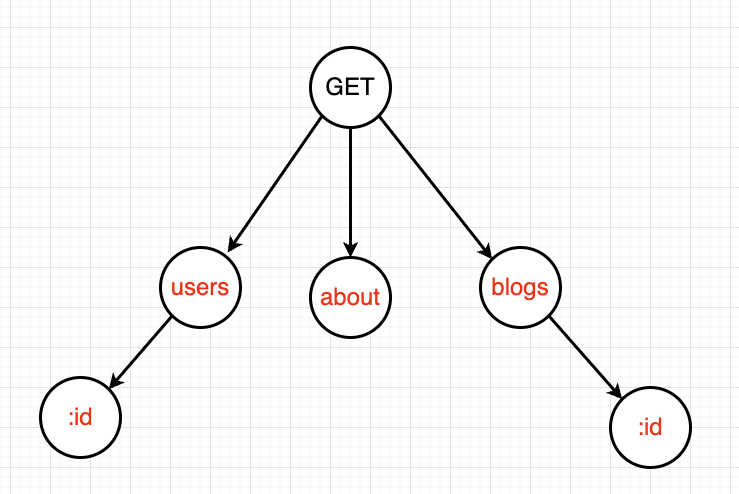
其中根节点是 http 请求方法,每个子节点都是路由中的一部分。
后面两个 :id 节点是通配符,可以匹配动态路由。
所以每个节点的结构如下:
1 | class RouterNode { |
结构中,path 字段表示完整的路径,只存于最后一个节点,表示一个完整的路径。part 表示路径中由 / 分隔的每一部分。children 存储的是子节点。isWild 标识该节点是否是通配符,level 标识节点的层级,在进行路由匹配时,层级要和路由中的 part 层级一致。
对于路由匹配功能来说,除了要存储路径这个前缀树,还要存储路由的处理函数,因此我们的路由 Router 大致结构如下:
1 | class Router { |
如上就基于前缀树实现了简单地动态路由匹配功能。
在使用时先添加路由,然后通过getRoute()方法就能查询到该路由对应的处理函数以及路由中的参数。
1 | router.addRoute("GET", "/blogs/*", function () { |